WildSight
Precision wildlife detection with deep learning
Motivation
Collisions between vehicles and animals present a significant issue in numerous countries, making it crucial to predict accidents and associated costs at regional and national levels for effective accident prevention (Gren & Jägerbrand, 2019).
Furthermore, a recent bear encounter at a clinic in Niigata Prefecture reflects a worrying trend of bears moving closer to human settlements in Japan. Due to a shortage of acorns, their primary food, and the spread of untamed vegetation, bears are increasingly foraging near human areas. A new term, “shin-sedai kuma” or “new-generation bears,” describes those born near human communities who are less afraid of people. This shift in bear behavior highlights the need for greater caution and a reassessment of human-bear interactions.
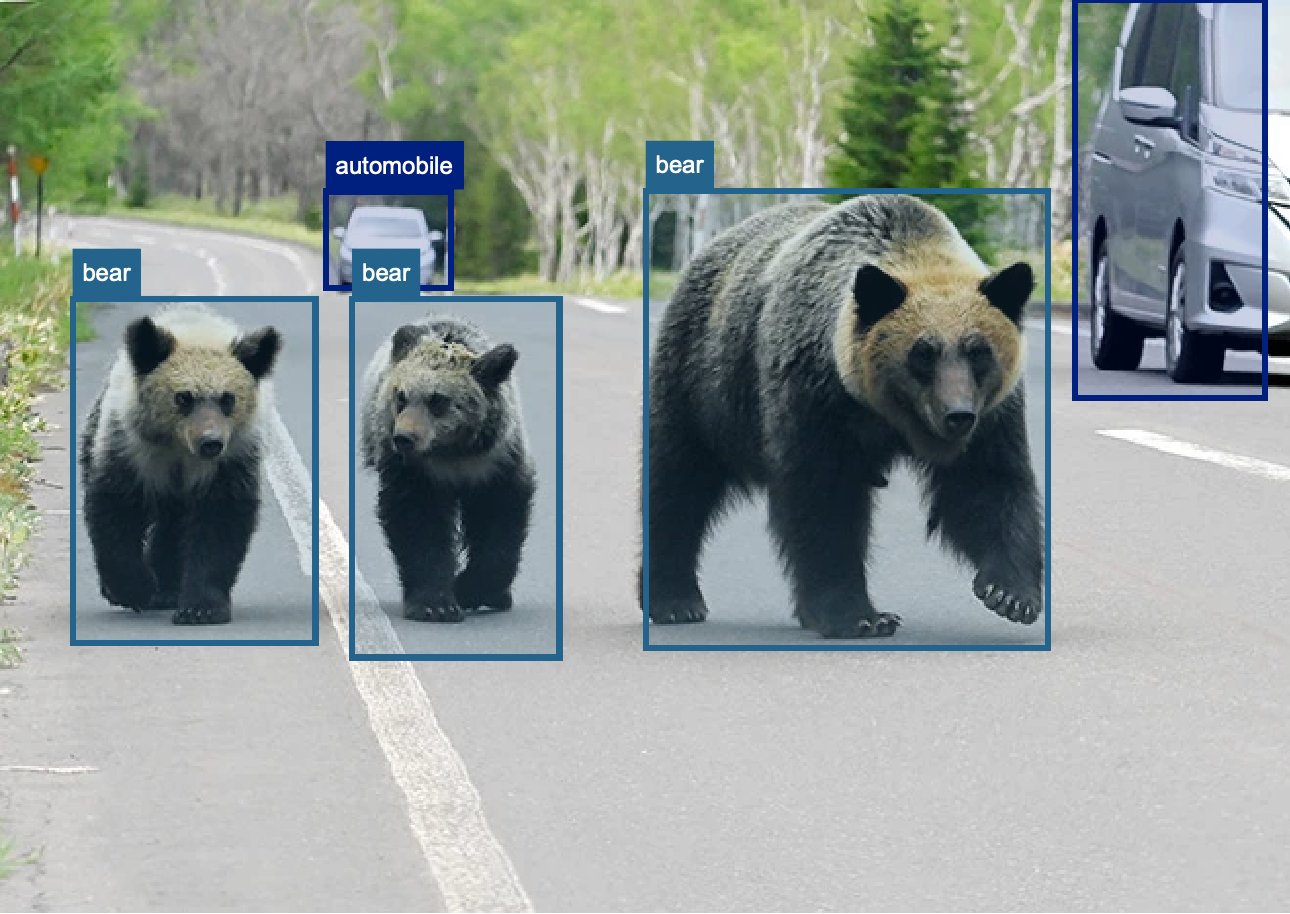
Objective
The goal of the WildSight project is to improve the accuracy and robustness of wild animal detection in complex field scenarios by using the YOLOv8 algorithm. The focus is on localizing and recognizing wild animals in different challenging environments, including scenes with multiple targets, small targets, or obstructed targets.
Prior Work
Previously, wild animal detection relied heavily on manual observation and feature-based algorithms, such as the HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients), and DPM (Deformable Parts Model) algorithms. These methods involved manually designed features and detectors, which were limited by their inability to achieve high accuracy and robustness in complex scenes. More recently, deep learning-based methods, particularly transfer learning techniques, have been used but lacked the real-time performance needed for field applications (Russo et al., 2024).
Benefits
-
Municipalities and safety authorities can deploy this technology to monitor and manage the presence of wild animals in urban or suburban areas. Early detection of animals near roads, residential areas, or public spaces can help prevent accidents, such as vehicle collisions with large animals, thereby improving public safety.
-
Other beneficiaries include biologists and researchers involved in wildlife monitoring and conservation. The approach can also be valuable to photographers, drone operators, and others involved in outdoor exploration and wildlife studies who require accurate and efficient animal detection in various environmental conditions.
Enabling Technologies
The key enabling technologies of the new approach include:
- YOLOv8 is a new real-time object detection algorithm that builds upon earlier YOLO versions, offering enhanced accuracy and speed, for images and videos.
- Data Augmentation Techniques to enhance the training dataset and improve model robustness.
Performance Criteria
The success of the new approach can be quantified through metrics such as precision, recall, mean Average Precision (mAP), and loss function trends during training. Additionally, the model’s ability to perform well in complex scenarios, such as detecting multiple, occluded, or small targets, serves as further evidence of its success.